What is human-centric cyber security risk?
Human-centric cyber security risk directly relates to people’s knowledge, attitudes and behaviours towards security. This risk is present in your organisation’s workforce, so it is important to identify and understand the cause so that you can take steps strengthen your security culture.
When every person in your organisation becomes an extension of your security team, you can move beyond standard compliance and create a cyber security culture of continuous improvement.
Why cyber security awareness training isn’t always enough
Learn how to identify the root cause of your organisation’s human-centric cyber risks and mitigate them with data-driven, targeted interventions.
Download factsheet (PDF 185KB)The importance of a strong cyber security culture
People, not technology, present the greatest vulnerability to an organisation’s security posture. Addressing this requires focused effort and investment in initiatives that reduce human-centric cyber security risk and uplift organisational security culture.

If you have anything less than a strong security culture, I’d urge you to consider the potential harm to your organisation, the harm to your staff and the harm to the national interest.1

Mike Burgess
Director General, ASIO
The three pillars of security
KPMG helps you to identify and evaluate your organisation’s human-centric cyber risks and risk drivers by looking at your organisation’s cyber security culture holistically. Our approach can help you to create measurable behavioural change that targets the key risk personas in your workforce.
All pillars are important but people are critical to each.
Process
Appropriate security policies and management systems.
Technology
Systems in place to mirror your security policies and risk appetite.
People
Adequately skilled members of the security team.
Organisational security culture
Organisations need a secure workforce not just a security workforce.
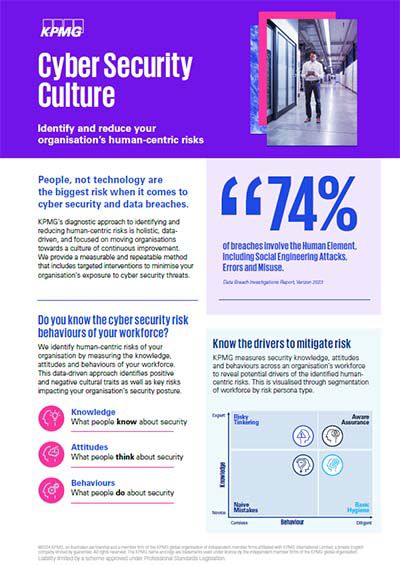
Knowledge
High levels of staff awareness and understanding of security policy, protocols and better practice.
Attitudes
Positive staff perceptions about security, articulated through their experience in the workplace.
Behaviours
Considered staff actions that impact security in the workplace.
Using data to measure cyber security culture
A data-driven approach can help you understand your organisation’s cyber security culture, the human-centric risks present in your workforce and the evidence based strategies to target them.
74% of all data and security breaches have a human element.2
Five steps to improving organisational cyber security culture
We remeasure your organisation’s cyber security culture over time to assess the effectiveness of the intervention strategies at reducing your human-centric cyber security risks. This provides your organisation with a data-driven Return on Investment mechanism.
-
Green flags
Increases in positive cultural traits -
Red flags
Reductions in negative cultural traits -
Evaluation of key risks
Indicate which risky behaviours have been mitigated by interventions
Qualitative and quantitative data collection to understand your organisation's current-state security operating model and cyber security culture, including:
- interviews with leadership, security teams and other stakeholders
- review of security policies, processes, training and awareness initiatives
- cyber security culture diagnostic survey gauging staff knowledge, attitudes and behaviours.
A comprehensive appraisal report of your cyber security culture, including:
- workforce segmentation by risk persona
- positive and negative cultural traits
- key behavioural risks.
Tailored intervention strategies that target the root cause of your human-centric cyber security risks, broken down by level of urgency.
-
Do now:
address key risks to security culture -
Do next:
address other significant risks -
Do later:
address additional risks for further uplift.
Implementation of the recommended intervention strategies. Interventions cover:
- All people
- Processes
- Technology elements
Build your cyber security culture with KPMG
KPMG’s approach to identifying and addressing human-centric cyber security risks is holistic, data-driven and focused on providing you with an evidence-based plan to move your organisation towards a culture of continuous improvement.
Learn more about security and cyber culture
To discuss how we can help you to build your organisation’s cyber security culture, contact us.
KPMG’s cyber culture specialists
Learn more about cyber security culture
References
- Director-General's Annual Threat Assessment 2024, ASIO, 28 February 2024
- 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, Verizon, accessed 29 April 2024




